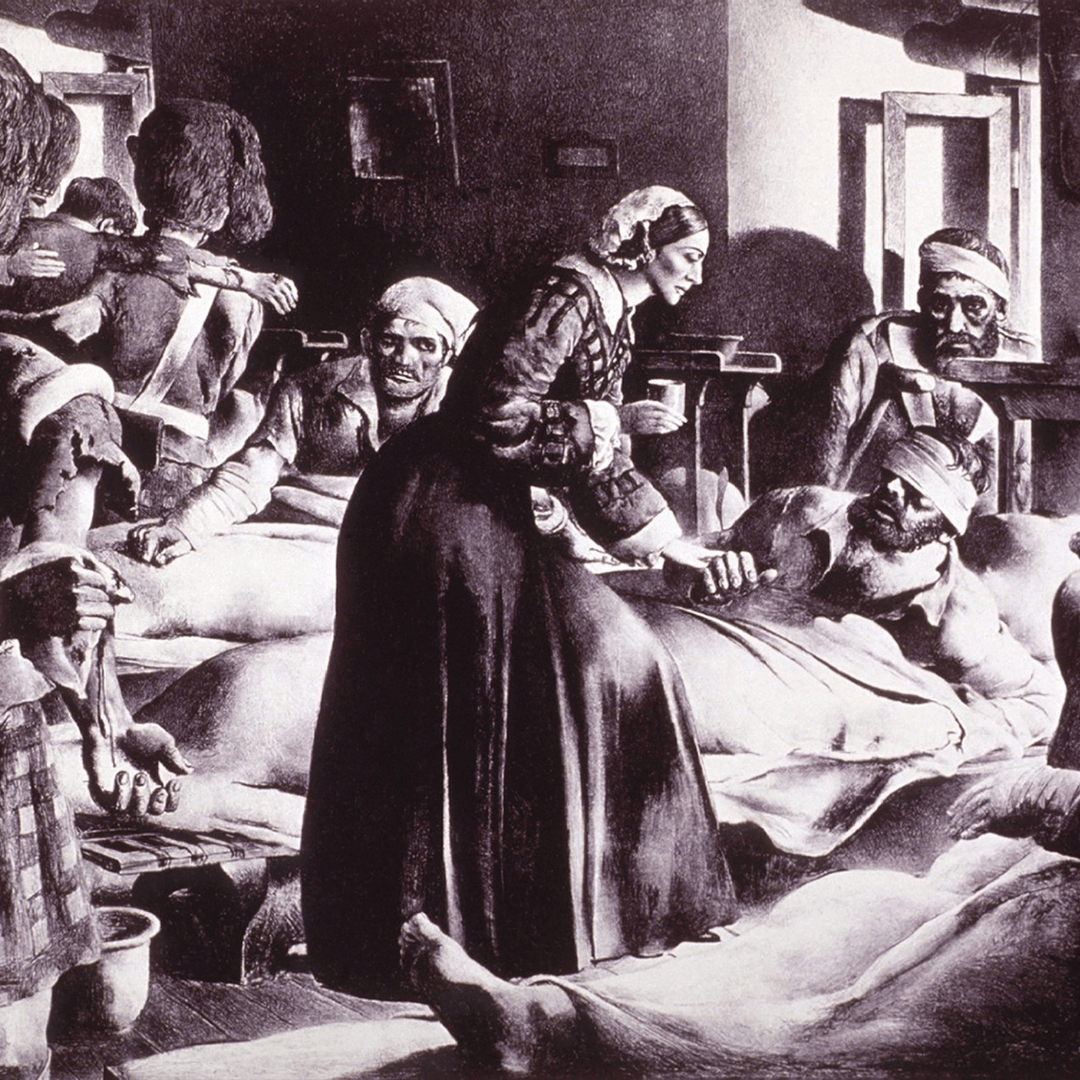
Florence Nightingale, the celebrated nurse who lived during the 19th century, is best known for her work in reforming nursing care and hospital administration – as well as her many contributions to improving healthcare worldwide. Her efforts not only resulted in a drastic decline in mortality rates of British troops during the Crimean War but also helped shift the perception of nurses from unskilled laborers to respected professionals.
Nightingale was ahead of her time and tackled issues that are still relevant today such as preventive health measures, the high cost of medical care, and advocating for better access to services. She implemented strict rules that improved hygiene standards among hospital staff, ensuring adequate nutrition and exercise for patients – all of which paid off with a remarkable 43% drop-in mortality rates at Scutari Hospital following her arrival in 1854.
In addition to these achievements, Nightingale wrote extensively on topics related to nurse training, public health statistics, patient outcomes, and even women’s rights. Her revolutionary ideas laid the foundation for modern nursing practices like evidence-based care and patient advocacy – making it clear how important she was in shaping what we know about nursing today. Furthermore, her legacy continues to live on through various awards presented every year by organizations such as the Red Cross or American Nurses Association (ANA).
To this day Florence Nightingale remains an iconic figure within healthcare circles who serves as an inspiration for nurses around the world – proving just how much of an impact one person can have when they dedicate their lives to helping others!